Originally developed for people with epilepsy, the ketogenic diet is today adorned with all the virtues: it would slow down neurodegenerative diseases ( Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s ), would fight against diabetes and cancer and even increase life expectancy.
The ketogenic diet is also said to lead to greater weight loss and lower cholesterol compared to a low fat diet. Other studies show that it is likely to lower the level of glucose concentration in the blood (HbA1c) below the diabetes threshold.
This diet was also the main treatment for diabetes before the appearance of insulin in the 1920s. Many athletes also practice the ketogenic diet to improve their performance and recovery.
In this beginner’s guide, you’ll learn everything you need to know about keto, and if it’s an ideal regimen for you.
What is keto diet?
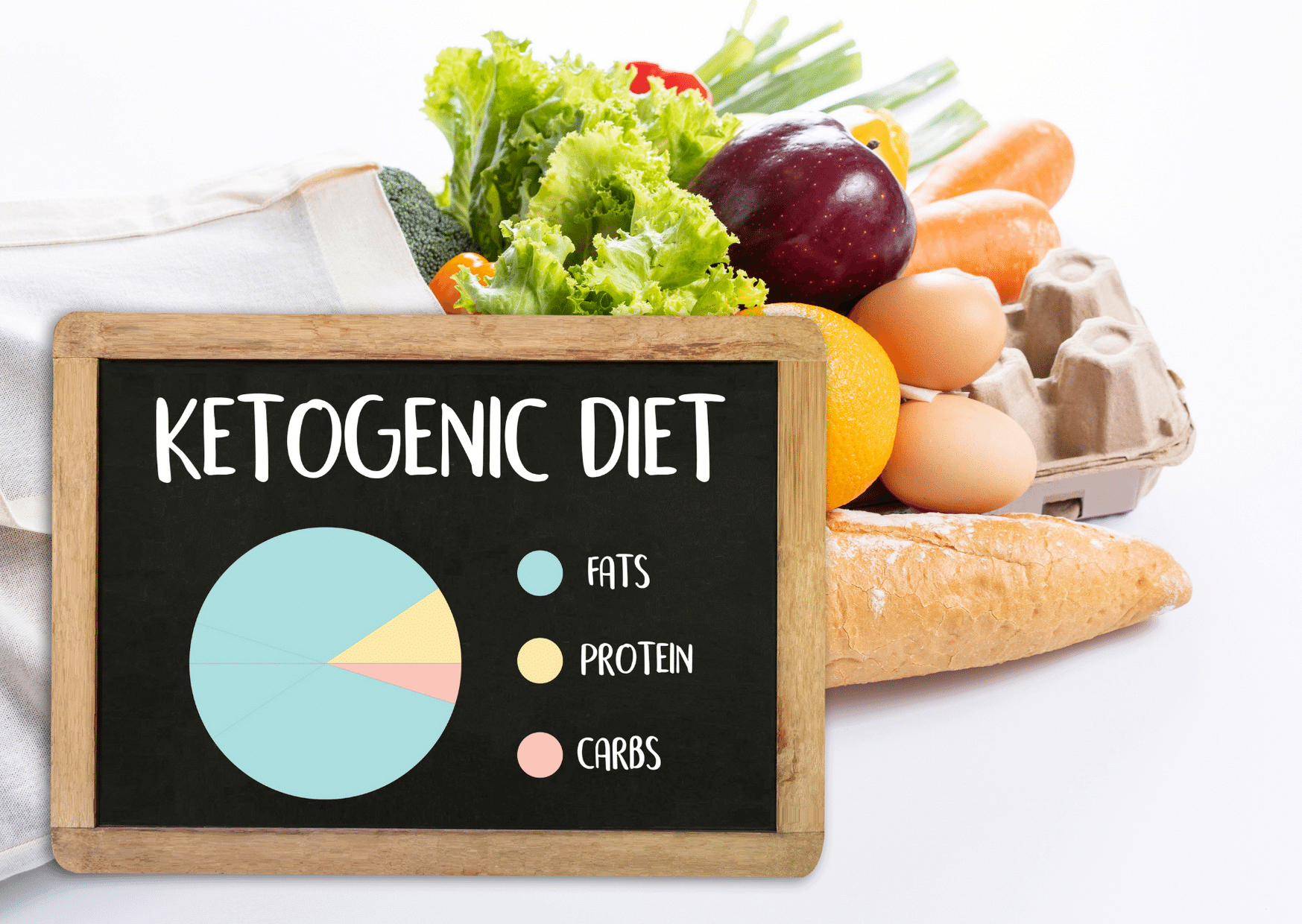
The ketogenic diet is composed of foods high in fat (70% to 90%) and low in carbohydrates (5% to 15%), which is almost the reverse proportions compared to a conventional diet (25% to 35% of fat and 45% to 55% carbohydrates). Protein intake remains unchanged.
When the body is deprived from carbohydrates, it begins to break down fat in the liver via ketogenesis, which then produces ketones. This is an alternative source of fuel for your body that can be used when blood sugar (glucose) is low. To get into ketosis quickly, you need about three days of low-carbohydrate diet (less than 50 g/d).
Keto diet for beginners
At the beginning, this caloric rebalancing requires several days of adaptation to the body: between 5 and 15 days on average.
The first 3 days are the most arduous, because the body must draw energy from fat, and no longer carbohydrates, which causes what is called a keto-flu: migraines, fatigue and nausea are on the program.
These symptoms can be similar to other low-calorie diets. In the case of the ketogenic diet, they are caused by a drop in sodium.
After 3 weeks of this diet, the body goes into a state of ketosis, that is to say, it will draw its energy from the ketone bodies and no longer from the carbohydrates.
Different types of ketogenic diets
There are several versions of the ketogenic diet to suit your goals and different types of metabolism:
Standard Ketogenic Diet: This is a very low-carb, moderate-protein, high-fat diet. It typically contains 75% fat, 20% protein, and only 5% carbohydrate.
Cyclical Ketogenic Diet: This diet includes periods of higher carb replenishment, like 5 ketogenic days followed by 2 high carb days.
Targeted Ketogenic Diet: This diet allows you to add carbs around workouts.
High Protein Ketogenic Diet: It is similar to a standard ketogenic diet, but includes more protein. The ratio is often 60% fat, 35% protein and 5% carbohydrate.
However, cyclical or targeted ketogenic diets are more advanced methods and primarily used by bodybuilders or athletes.
Keto Diet Foods
Fat takes up 75% of the recommended daily allowance for the ketogenic diet. But not all fats are good for the body.
Recommended fats: monounsaturated fats such as olive oil, almonds, walnuts, avocados. Saturated fats contained in red meat, high-fat dairy products (avoid yogurts and cottage cheeses with 0% fat).
Fats to avoid: all omega-6 (sunflower, soybean, grape seed, peanut oils…etc) which have a pro-inflammatory action in the body when consumed in large quantities. They can thus increase our chance of increasing diabetes, cardiovascular disease, asthma and obesity. Also, saturated fats included in cold meats, pastries, fried foods are to be avoided.
Fats to be consumed in moderation: omega-3s (sardines, salmon, flax seeds, walnuts, etc).
By respecting the caloric proportions, you can therefore develop your menus on the basis of the following foods, rich in good lipids and / or low in carbohydrates:
What to Eat on Keto Diet?
The majority of your meals will consist of these foods:
Meat: red meat, steak, ham, sausage, bacon, chicken and turkey
Fatty fish: like salmon, trout, tuna, and mackerel
Eggs: Look for whole eggs that are grazed or high in omega-3s
Cheese: Cheeses rich in calcium (cheddar, goat cheese, cream, blue cheese or mozzarella)
Nuts and seeds: almonds, walnuts, flax seeds, pumpkin seeds, chia seeds, etc.
Healthy oils: Mainly extra virgin olive oil, coconut oil and avocado oil
Avocados: whole avocados or freshly made guacamole
Low-carb vegetables: most greens, tomatoes, onions, peppers, broccoli…etc.
Condiments: You can use salt, pepper and various healthy herbs and spices
Foods to Avoid
Sweet foods: soda, fruit juices, smoothies, cakes, ice creams, candies, etc.
Cereal or starches: wheat products, rice, pasta, cereals, etc.
Fruits: Most fruits are banned on the keto diet except for a few low-carb fruits like strawberries, raspberries and blackberries. Check out these 8 keto-friendly fruits!
Beans or legumes: peas, kidney beans, lentils, chickpeas, etc.
Root vegetables: potatoes, sweet potatoes, carrots, parsnips, etc.
Low fat or diet products: these are highly processed and often high in carbohydrates.
Certain condiments or sauces: these often contain sugar and unhealthy fats.
Unhealthy fats: limit your intake of processed vegetable oils, mayonnaise, etc.
Alcohol: due to their carbohydrate content, many alcoholic drinks can throw you out of ketosis.
Sugar-free diet foods: these are often high in sugar which can affect ketone levels in some cases. These foods also tend to be highly processed.
A typical ketogenic menu
Lunch: 150g of rice + 150g of broccoli + 80g of salmon + 10g of olive oil
Snack: 1 avocado + a hot drink with 20g of coconut oil
Dinner: 150g of sweet potato + 150g of rice + 125g of steak + 10g of olive oil + 100g of raspberry
Note that the quantities are indicative, they are to be modified according to your diet and your daily caloric need.
Can the ketogenic diet help you lose weight?
Research has shown that low-sugar diets allow you to lose weight faster than low-fat diets. But in the long term, the weight curves come together.
Dietitian’s thoughts on the keto diet
In terms of weight loss, the ketogenic diet has been shown to be more effective than a low fat diet. Indeed, many studies have compared diets low in fat or high in protein and moderately high in carbohydrates with the ketogenic diet.
The results that show in the short term (1 year and less), are promising. On the other hand, very few studies have evaluated the effects of the ketogenic diet in the longer term.
Most dietitians agree that the keto diet does not respect the basic rules of a balanced diet. It excludes many food groups such as cereal products, legumes and fruits which can lead to fibers, vitamins, and anti-oxidants deficiencies.
Nevertheless, some people believe that switching from a standard high-carb diet to a paleo or low-carb diet is enough to lose weight with ketosis. But it’s not always the case. It’s important to make sure you’re using ketones rather than carbs. Otherwise, you are not going to burn fat or lose weight.
The key to ketogenic diet results is consistency. This means eating ketogenic foods including healthy fats, quality vegetables, and meats.
Before embarking on your ketogenic weight loss journey, it’s important to consult with a doctor or your personal dietitian to increase your chances of success.
- Comparing the Efficacy of Ketogenic Diet with Low-Fat Diet for Weight Loss
- Beyond weight loss: a review of the therapeutic uses of very-low-carbohydrate (ketogenic) diets
- Ketogenic diets for weight loss: A review of their principles, safety and efficacy
- Clinical aspects of the ketogenic diet
- Very-low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet v. low-fat diet for long-term weight loss: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials
- Effects of a high-protein ketogenic diet on hunger, appetite, and weight loss in obese men feeding ad libitum
- Comparison of a very low-calorie-ketogenic diet with a standard low-calorie diet in the treatment of obesity