Bariatric surgery or weight loss surgery has become a mainstream surgical treatment for morbid obesity. This surgery causes weight loss because it restricts the amount of food that the individual eats and / or the absorption of nutrients at the intestinal level, depending on the procedure used.
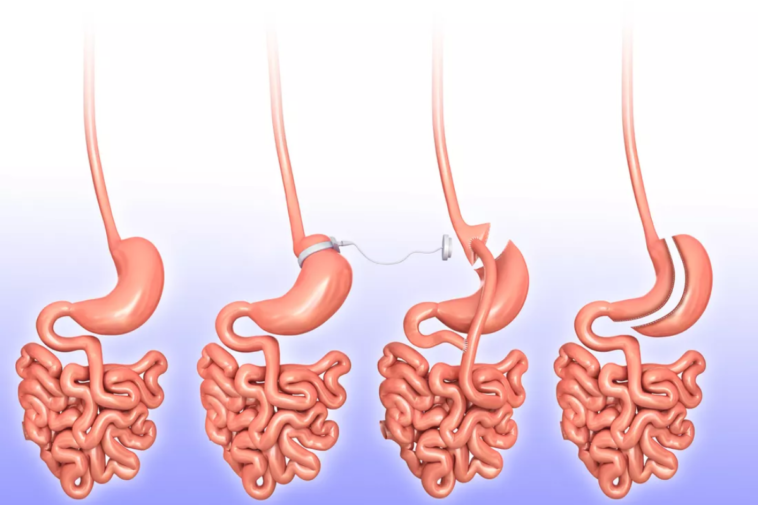
There are several types of bariatric surgery, the main ones being the gastric bypass, the sleeve and the gastric band. Each procedure has different requirements, advantages and disadvantages, which is why the surgeon will evaluate which is the best method according to the characteristics of each individual.
Continue till the end, and learn more about the requirements, cost, and health risks associated with weight loss surgery.
Requirements for bariatric surgery
Bariatric surgery is applicable in the case of morbid obesity when the BMI is greater than or equal to 40 Kg / m2 OR when the BMI is greater than or equal to 35 Kg / m2 with associated comorbidities such as diabetes, sleep apnea, hypertension, dyslipidemia, cardiovascular conditions, severe uncontrolled asthma, osteoarthritis, herniated discs, gastroesophageal reflux with surgical indication, calculous cholecystopathy, recurrent acute pancreatitis, hepatic steatosis, female stress urinary incontinence, infertility, erectile dysfunction, polycystic ovary syndrome, varicose veins and hemorrhoidal disease, idiopathic intracranial hypertension, social stigma, and depression.
This type of surgical procedure is indicated by the doctor when the individual tried to lose weight through clinical and dietary treatments, and did not obtain the expected results for at least two years.
After the surgery, it is necessary to follow a rigorous diet and practice physical activity regularly, to promote weight loss and proper body function.
The cost of weight loss surgery
The cost of weight loss surgery varies from surgeon to surgeon. It can range from $15,000 to over $40,000, if the surgery is successful and there are no complications. If a patient’s insurance covers this type of surgery, they’ll need to be pre-approved, a process that requires the involvement of both the surgeon and the primary care physician to document the surgical needs. The process is usually starts during the initial consultation with an obesity surgeon.
If the patient is paying in full for their surgery, there are additional charges for blood tests, x-rays, anesthesia, nursing care, medication, hospital expenses in addition to the surgeons fees.
Types of bariatric surgery
There are several bariatric operations that can be done to lose weight. You must remember that these surgical operations are not a panacea, and a patient must follow their surgeon exact guidelines.
Yes, weight loss surgeries are effective, but they also have risks and require a long-term commitment to change one’s health, and apperance.
Let’s look at the different procedures one by one:
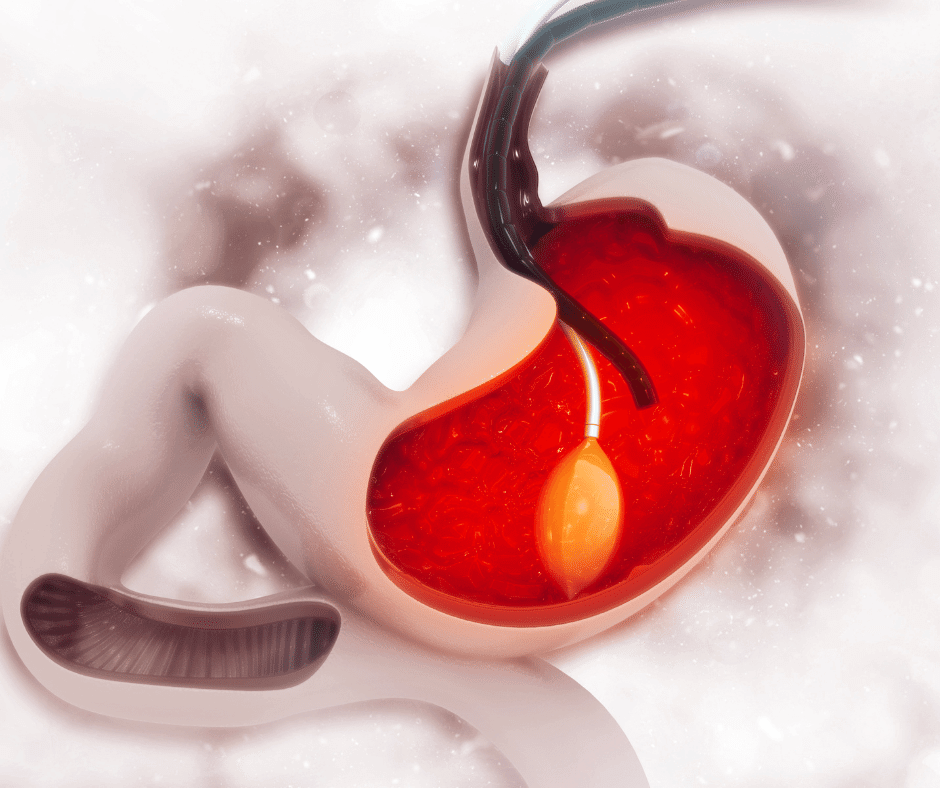
Intragastric balloon
The intragastric balloon is intended to reduce the volume of the stomach, thus our food consumption. Intragastric balloon It consists of introducing a ball of saline solution into the stomach with the intention of reducing its volume by half.
By decreasing gastric volume, the feeling of satiety is gained earlier, thus decreasing the daily food intake of the patient. The operation is quite safe; does not require hospitalization, anesthesia, and does not usually have complications.
The deflated balloon is inserted endoscopically and, once inside the stomach, it is inflated with saline and the valve is sealed. Although there is already a more advanced method: the ingestible intragastric balloon. It would be enough to swallow a capsule attached to a thread. Once in the stomach the balloon would swell. A much less noticeable method.
The balloon is left in the stomach for about 6-8 months and an average of two pounds is lost per week, although this varies by patient. In addition to cutting calories, the key is to re-educate our eating habits so that when the ball is removed, the patient is able to maintain a healthy weight.
Gastric band
An inflatable band is placed around the upper part of the stomach, creating a kind of small stomach. Again, the objective of this intervention is to decrease the volume of the stomach so that the feeling of satiety appears earlier. Moreover, the band prevents the stomach from expanding too.
The passage of food from the smaller stomach to the rest of the stomach will be made little by little through a small hole, the diameter of which is regulated by the filling of the band with saline serum. A first swelling of the band is usually performed around the sixth week, then it only swells if the patient stagnates in weight loss.
This operation does not require hospitalization or anesthesia, but it is somewhat more invasive than the intragastric balloon, since it requires laparoscopy (small incisions in the abdomen where the band is inserted and placed) and some points to fix the band to the stomach.
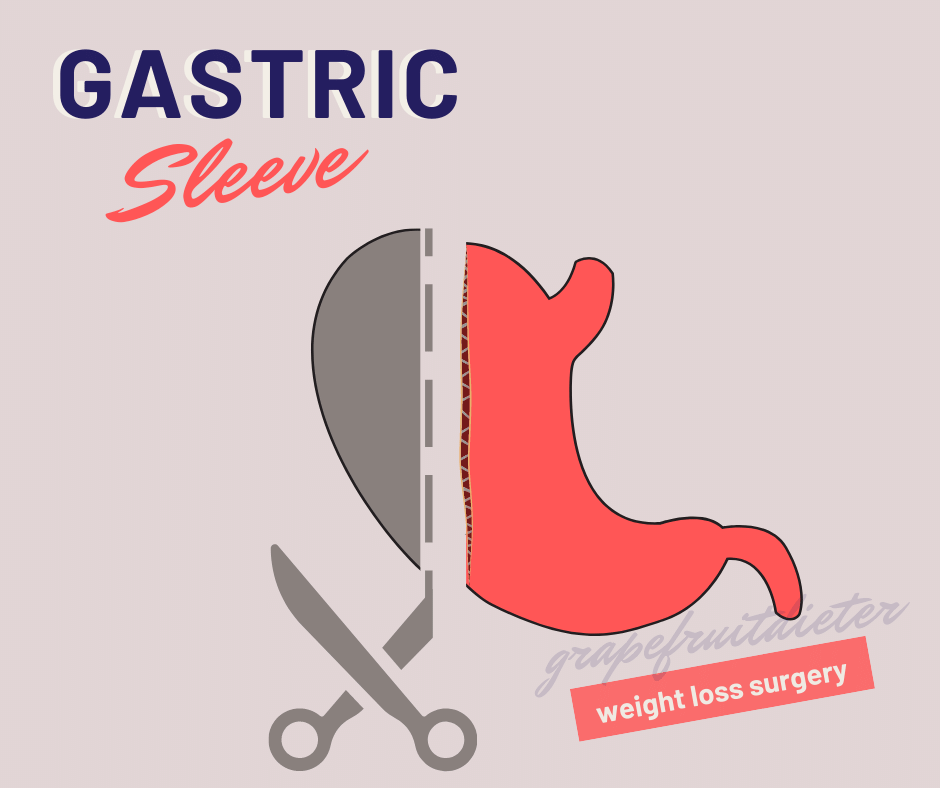
Gastric sleeve
Here we already enter into more invasive surgery and, although it is done by laparoscopy, the size of the stomach is reduced by removing part of it (gastrectomy), by 75-80%. The stomach is cut vertically and stapled, forming a “sleeve” the size of a banana.
This operation lasts between one and three hours and does require hospitalization: between two to three days. The stomach retains all its functions, it has simply reduced its volume considerably, so the feeling of fullness will appear earlier.
The weight loss with this operation is greater than that achieved with the gastric band, although less than that which would be achieved with a gastric bypass, but the risks and side effects are lower, since here we are conserving part of the stomach. Unlike what is done with gastric bypass, where the stomach no longer receives food and it goes directly to the intestine.
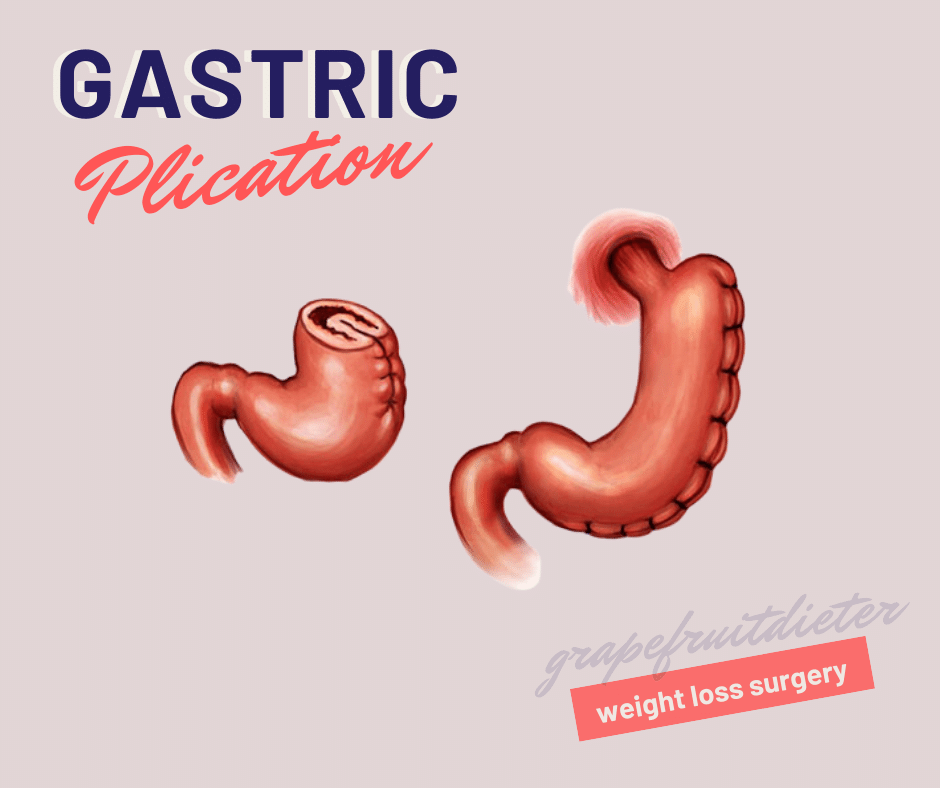
Gastric plication
This operation is similar to the previous one, unlike the fact that there is no gastrectomy but gastroplasty, by folding the stomach on inwards, reducing the volume of the stomach but preserving it in its entirety.
The stomach preserves all its functions and its volume is reduced by 75-80%. It does require short hospitalization of one day and is a reversible operation. Stitches are usually removed after a year and a half or two years.
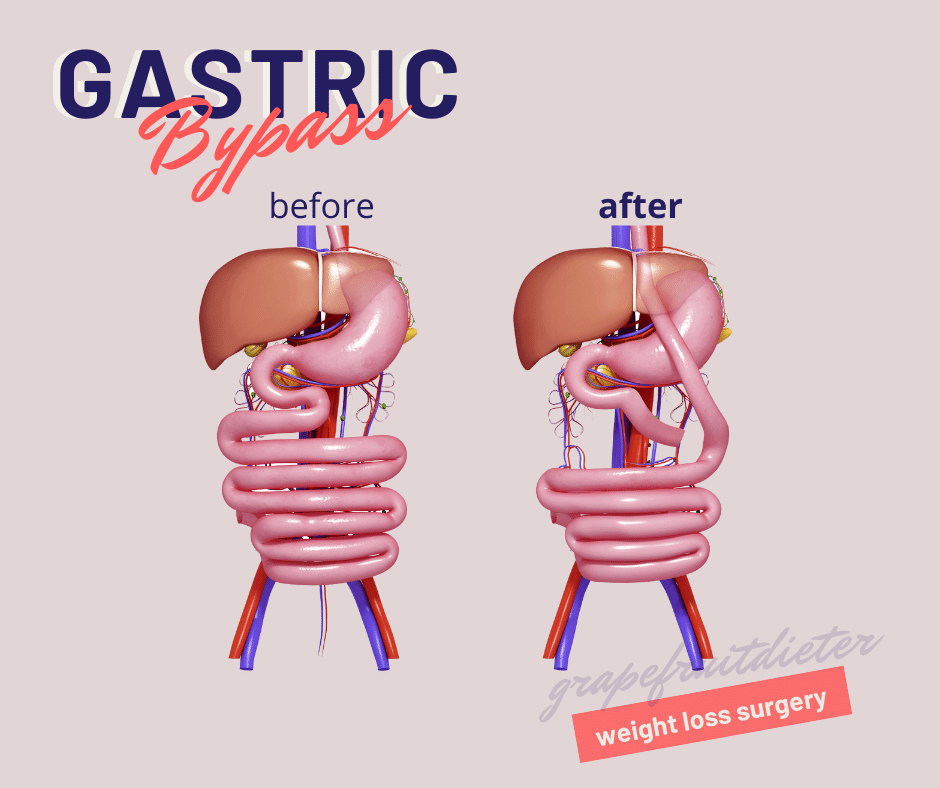
Bypass or gastric bypass surgery
Across surgeries, this method is one of the most effective, since it directly joins the upper portion of the stomach with the small intestine (duodenum), leaving aside the stomach, which is not removed, it is left in place, but food will no longer pass through it.
This technique is so effective for the following reasons: the size of the stomach is considerably reduced (satiety decreases), absorption is also decreased and the insulin response is reduced. Three fundamental aspects so that the body does not accumulate, but begins to lose reserves.
In a matter of a year, 75% of the excess weight that the patient has can be lost, although it all depends on the habits of the patient after the surgery. The operation usually lasts about three hours and requires hospitalization for at least one day.
Abdominoplasty
We can consider this operation an aesthetic operation, since it does not affect the digestive processes, but directly removes excess fat and skin from the abdomen, which is usually the part where it accumulates the most.
This operation requires general anesthesia, and there is no laparoscopy, it is a more invasive method where the skin of the abdomen is released with a scalpel, removing the excess fat and skin, even the abdominal muscles are reinforced with sutures if they are very flaccid.
The operation usually requires general anesthesia, lasts about 2-4 hours and after the operation patients have to wear a girdle to further support the stomach. Here, even in a minimal way, there are scars and it takes a while for the abdominal shape to be homogeneous.

Liposuction
This can also be considered an aesthetic operation. It is one of the most popular surgeries to when it comes to removing fat from the middle of the abdomen, but it is useless if we continue with bad eating habits, since nothing is intervened on the digestive system.
It works by extracting fat using a syringe that aspirates it. The problem here is that when there is a significant reduction in fat, there will be excess skin and aesthetically it does not look pretty, so another operation will have to be done later to reduce that excess skin.
The surgery may not require hospitalization but your surgeon may require you to wear a compression girdle to alleviate any swelling.

How is the post-operative
The postoperative period of bariatric surgery will depend on the type of surgery performed, however, in any of them a rigorous nutritional control must be maintained, starting with a diet of clear liquids that will evolve according to the tolerance of the individual. In addition to this, in those techniques where a malabsorption of nutrients occurs, the nutritionist will indicate the intake of multivitamin supplements, calcium, iron and vitamin B12 to avoid the deficit of these nutrients, preventing problems such as anemia, hair loss, weakness in the nails, among others.
Women who want to become pregnant after surgery must wait at least 18 months, because accelerated weight loss could impair the development of the baby.
Possible risks of bariatric surgery
The risks of bariatric surgery are associated with the severity of the diseases that the individual presents, so the main complications are:
- Pulmonary embolism, which is the obstruction of a blood vessel in the lung, causing severe pain and shortness of breath
- Internal bleeding in the region where the surgery was performed
- The formation of a fistula, which is an abnormal connection between two organs, originating mainly where the resection was performed at the intestinal level
- Vomiting, diarrhea, and bloody stools
These complications typically arise during a hospital stay and are resolved quickly by medical staff. However, depending on the severity of the symptoms, a new operation may be necessary to correct the problem.
In addition, it is common for patients to have nutritional complications after bariatric surgery such as anemia, deficiency of folic acid, calcium, and vitamin B12. In addition, severe malnutrition can also occur, in case a regular control with the nutritionist is not maintained.
Next, discover what foods to eat after a bariatric surgery?
This article is intended for general informational purposes only. Please consult with a licensed physician for professional medical advice. If you take whatever action based on the material presented is solely at your own risk, and responsibility (disclaimer).
- Bariatric surgery for severe obesity. Consumer information sheet. National Institute of Diabetes, Digestive and Kidney Diseases. March 2008. http://win.niddk.nih.gov/publications/gastric.htm
- Jones, Nicolas V. Christou, MD, Ph.D., Didier Look, MD, and Lloyd D. MacLean, MD, PhD. “Weight gain after short and long limb gastric bypass in patients followed for more than 10 years.” Annals of Surgery 2006 November; 244 (5): 734-740.
- Mayo Clinic bariatric surgery types: Biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch (BPD/DS) gastric bypass (Roux-en-Y) sleeve gastrectomy https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/bariatric-surgery/about/pac-20394258